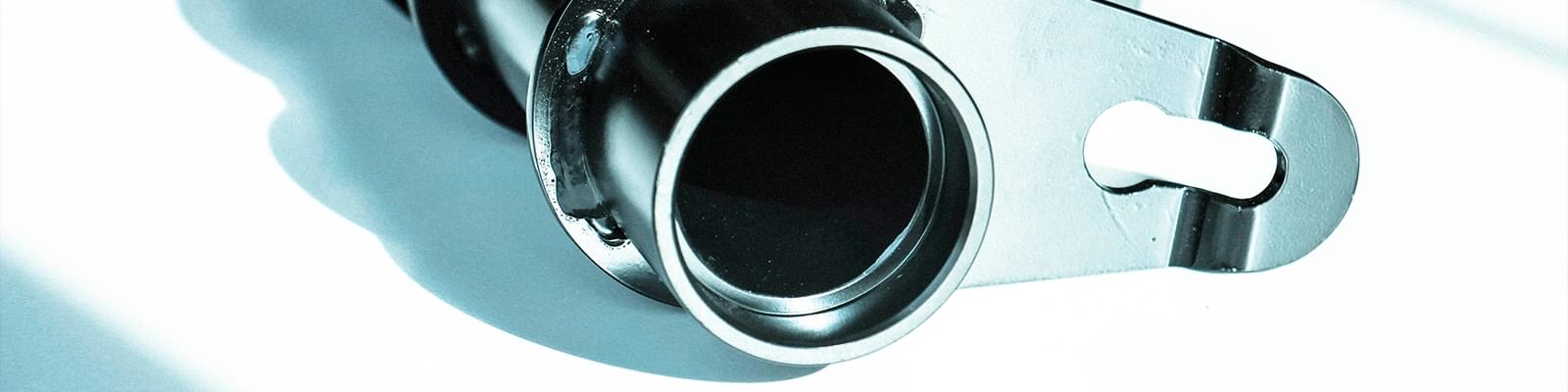
Metal surface treatments
Minifaber employs suppliers specialised in cold sheet metal forming and surface treatments for metal.Minifaber employs suppliers who have extensive know-how in the in the surface treatment of metals. The purpose of these metal treatments is to grant the product an excellent finish that, not only provides aesthetic value, but increases its durability, eliminating harmful oxidation processes.
Specifically, Minifaber can provide the surfaces treatments listed below on aluminum, steel and stainless steel, copper, iron and special alloys.
What will you find on this page?
- Metal galvanising
- Metal nickel plating
- Metal chrome plating
- Metal silver plating
- Metal burnishing
- Metal phosphatization
- Metal painting: cataphoresis – powdering
- Metal polishing
- Metal peening
- Metal sanding
- Metal anodizing
- Stainless steel electro-polishing
- Why steel surface treatment may be required
Metal galvanising
In general, zinc plating is the process by which a metal artefact is coated with zinc ("galvanised") in order to preserve it from galvanic corrosion. There are several steps to follow to perform this metal surface treatment: the most common method is hot-dip galvanising, in which the object to be galvanised is immersed in a zinc bath at 842°F, from which it will come out coated in both the external and internal surfaces. Through the galvanic process an iron-zinc alloy is formed, much more resistant than a normal coating film and hardly corrupted by external agents. There are also other galvanising processes: cold and spray galvanising, methodologies that do not actually have the same features in terms of final quality and durability when compared with hot-dip galvanising. Potentially, any metal artefact can be protected by undergoing this process, even if galvanizing is most used as steel surface treatment.
Metal nickel plating
Like galvanising, also nickel plating is a surface finish that involves the dipping of the metal artefact in a nickel bath, in order to make it much more durable and corrosion-resistant, typical features of nickel. Nickel plating distinguishes between electrolytic nickel plating and chemical nickel plating, the second one being more precise and better fitting to the geometry of the piece, which is why it is much more widespread.
Metal chrome plating
The coating of a metal object from a thin layer of chromium can have both decorative and functional functions. This metal surface treatment is obtained through galvanic deposition in an electrolytic bath. The chromium plating aims at preventing the passivation (corrosion) of the metal object, improving its resistance and durability. The chromium bath is usually performed in a chemical compound such as chrome acid or chromium trioxide.

Metal silver plating
Silver plating is carried out by galvanic or electrolytic process and, like other surface treatments for metal, is based on the same principles of galvanising or chromium plating. This process makes it possible to obtain an excellent result, due to the conductive and protective qualities of silver. In addition, it is also possible to operate a delimited and selective silvering of particular areas of interest on one piece. To block the process of sulphurization, typical of silver, it is necessary to make a further step with a process of passivation.
Metal burnishing
Normally used to improve the aesthetic appearance of already worked parts and to protect against corrosion of atmospheric agents, burnishing is that chemical treatment that darkens in the particular shiny black-blue colour iron and carbon steel artefacts. In the past, this process was obtained in a very coarse way, exposing the piece to be burnt directly on flame, moving it when it had reached the desired shade of blue. Today it is carried out through galvanic treatments and immersion in chemical baths.
Metal phosphatization
Phosphatization is a common metal surface treatment for iron and ferrous alloys, as well as universally used as a preparation treatment for the painting of steel sheet in the automotive industry. Phosphatization is a chemical process in which the surface of a metal material is altered by the phosphate crystals that bind chemically to the metal substrate, improving its properties in terms of resistance to corrosion and wear.

Metal painting: cataphoresis – powdering
Varnishing treatment that significantly increases the corrosion resistance of metal objects or current conductors through the coating of an epoxy or acrylic resin. This surface treatment ensures greater protection against rust of metal. It is a very widespread technique in the automotive industry.
Metal polishing
Among the surface treatments of metals, polishing is the least invasive. Polishing is a finishing method that uses an abrasive material to smooth surfaces and gives the metal a glossy and smooth final effect. Surface finishing treatment of metals that gives a glossy and smooth final effect. It is usually done starting from an initial phase in which the artefact is processed by deep cleaning (grinding or passage with abrasive paste) to be descaled and polished on the entire surface.
Metal peening
Peening is the process of working a metal's surface to increase the fatigue resistance of metal components, by blasting with shot (shot peening), or focusing light (laser peening). Peening is used to increase the fatigue resistance of metal components. The blasting occurs through the violent cold jet of spherical balls on the artefact, causing a microscopic plastic deformation that helps to sustain residual tension.
Metal sanding
Metal surface treatment that, in some ways, is similar to metal peening, even if in the metal sanding the most superficial part of the metal object is hit violently by a jet of sand and air. The purpose is to completely remove a particularly ruined/corroded area of a metal surface. The same procedure is applied on a compact disc to avoid retrieving data that it contains.
Metal anodizing
 Anodizing changes the microscopic texture of the surface and the crystal structure of the metal near the surface. In anodizing a protective oxide layer is formed on the metal surface. The process is induced by electroplating and is commonly used on aluminum, zinc, magnesium and other metals.
Anodizing changes the microscopic texture of the surface and the crystal structure of the metal near the surface. In anodizing a protective oxide layer is formed on the metal surface. The process is induced by electroplating and is commonly used on aluminum, zinc, magnesium and other metals.
Stainless steel electro-polishing
The electro-polishing of stainless steel is a surface treatment that consists in removing the surface layer of stainless steel (between 10 and 40 microns) in order to make it more resistant to corrosion. As a treatment in which the material is removed instead of applied, it is also referred to as " reverse galvanic process of deposition".
Why steel surface treatment may be required
Now, let's take a brief look at why a specific steel surface treatment may be required.
Steel can undergo a corrosion process over time if it is not treated properly, which compromises its strength and structure, as well as its aesthetics.
There are several types of corrosion:
- Uniform corrosion, that involves the deterioration of the entire exposed surface of steel. This type of corrosion is caused by a chemical or electrochemical reaction that causes deterioration of the entire exposed surface of the steel. The best way to protect steel from uniform attack corrosion is to subject the steel to a surface treatment that creates a protective barrier between the steel and the outside.
- Galvanic corrosion, or corrosion of dissimilar metals, occurs when steel comes into contact with another metal in a corrosive electrolyte. The best way to avoid it is to make sure dissimilar metals are not in direct contact.
- Crevice corrosion is localized, usually in a stagnant microenvironment where acidic conditions or oxygen depletion in a crevice can lead to corrosion. Subjecting steel to a specific surface treatment can prevent it from being corroded.
Pitting corrosion occurs when localized areas of steel lose their protective layer. This area becomes anodic, while some of the remaining metal becomes cathodic, producing a localized galvanic reaction. To avoid it, one must be especially diligent with steel and reapply protective coatings regularly, or use cathodic protection.
Minifaber finishes metal surfaces for the following industries:
- Electromechanics
- Vending
- Kitchen robots
- Medical
- Gas distribution
- Professional lighting
- Home appliances
Minifaber has evolved to become the only company able to design and manufacture the complex, assembled end products no one else can.
Find out more